China’s foreign trade continued its steady and positive momentum.
Xinhua News Agency, Beijing, May 9th Title: China’s foreign trade continues its steady and good momentum.
Xinhua News Agency reporters Liu Fei, Zhou Wenqi and Xin Guo.
According to data released by the General Administration of Customs of China on the 9th, in the first four months of this year, the total import and export value of China’s foreign trade reached 13.32 trillion yuan, up 5.8% year-on-year, and the growth rate was 1 percentage point faster than the 4.8% in the first quarter. Among them, the monthly import and export in April was 3.43 trillion yuan, an increase of 8.9%.
In terms of breakdown, in the first four months of this year, China exported 7.67 trillion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 10.6%; Imports reached 5.65 trillion yuan, up by 0.02%.
Bai Ming, a member of the Academic Degrees Committee of the Ministry of Commerce of China, said that in recent months, with the overall demand of the United States, Europe and Japan slowing down, the scale of China’s foreign trade maintained steady growth, and the growth rate still exceeded expectations, indicating that China’s foreign trade was full of resilience.
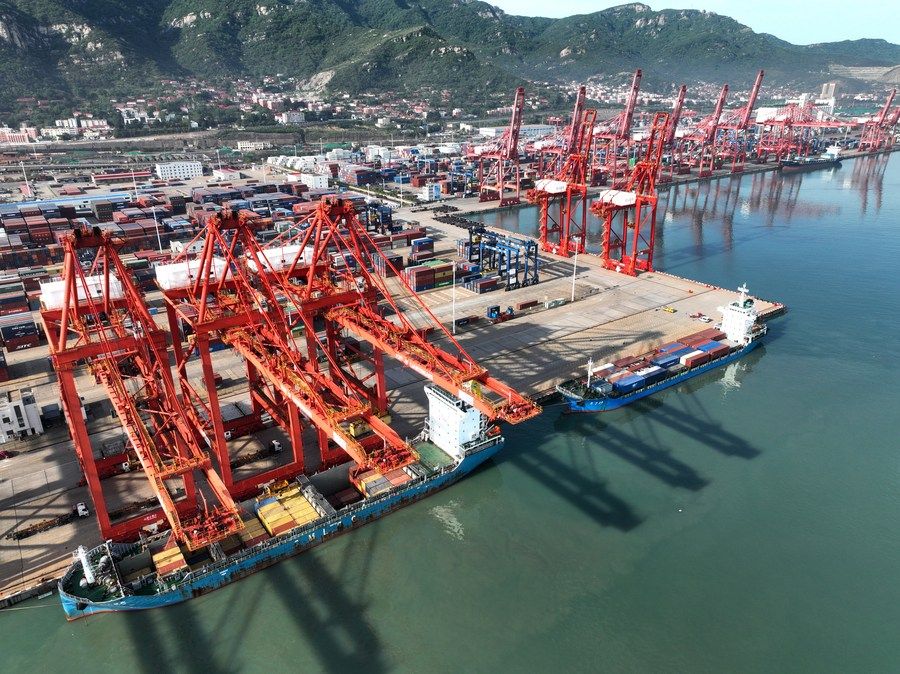

On May 9, at the container terminal in Lianyungang Port, Jiangsu Province, the cargo ship docked at the berth to load and unload containers (photo of drone). Xinhua News Agency (photo by Wang Chun)
In the first four months, the import and export of general trade was 8.72 trillion yuan, up 8.5% year-on-year, accounting for 65.4% of China’s total foreign trade; The import and export of private enterprises reached 7.05 trillion yuan, up 15.8% year-on-year, accounting for more than 50% of China’s total foreign trade.
Experts interviewed here generally believe that, despite the adverse factors such as the downward pressure of the world economy and poor demand in overseas markets, China’s foreign trade has continued steadily and its foreign trade structure has been continuously optimized since the smooth transition of epidemic prevention and control.
According to the data of the General Administration of Customs, in the first four months, China exported 4.44 trillion yuan of mechanical and electrical products, up 10.5% year-on-year, accounting for 57.9% of the total export value. Among them, driven by the export of new energy vehicles, automobile exports increased by 120.3% year-on-year.
In the first quarter of this year, the export of "new three products" such as electric manned vehicles, lithium batteries and solar cells increased by 66.9% year-on-year, which boosted the overall export growth rate by 2 percentage points.
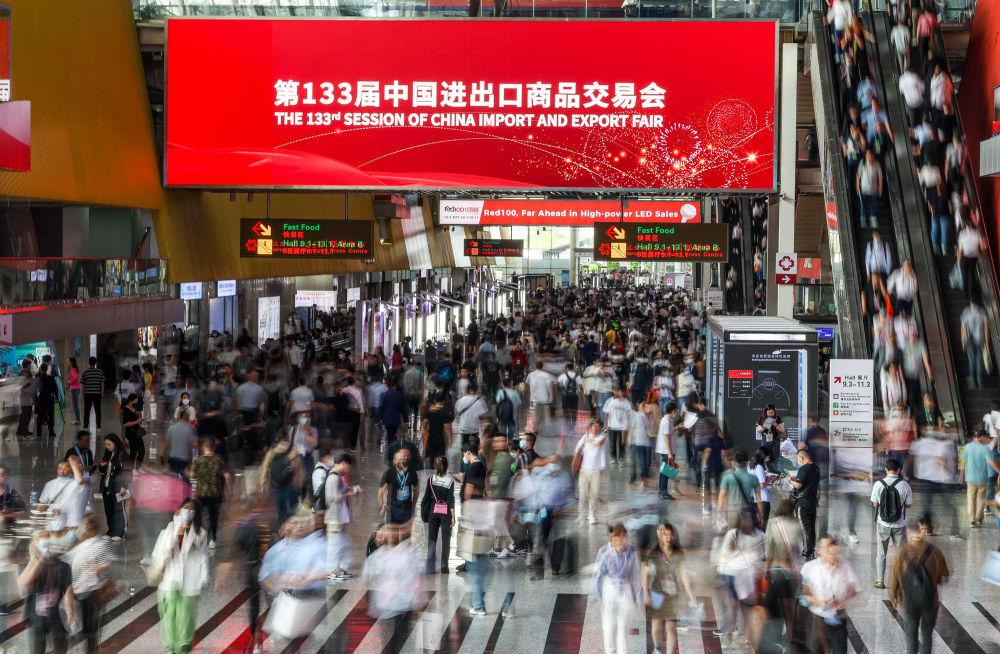

This is the scene of the 133rd Canton Fair filmed on April 15th. Xinhua News Agency reporter Liu Dawei photo
At the 133rd Canton Fair, which ended a few days ago, a large number of new products, new technologies and new processes were exhibited for the first time. High-end, intelligent, customized, branded and green low-carbon products were favored by buyers all over the world, highlighting that China manufacturing is constantly moving towards the high end of the global value chain, showing the resilience and vitality of China’s foreign trade.
Experts in the industry believe that such high-tech, high value-added products that lead to green transformation have become new growth points for exports, reflecting China’s efforts to achieve effective quality improvement and reasonable growth in quantity at the export level, which is an important manifestation of high-quality development of foreign trade.
In recent years, China’s import and export show the characteristics of huge total trade in goods, innovative development of service trade, flourishing new formats, multi-point market flowering and gradual optimization of structure.
Including cross-border e-commerce, bonded logistics, bonded maintenance, overseas warehousing, offshore trade, etc., are the effective force of China’s foreign trade development and an important trend of international trade development.
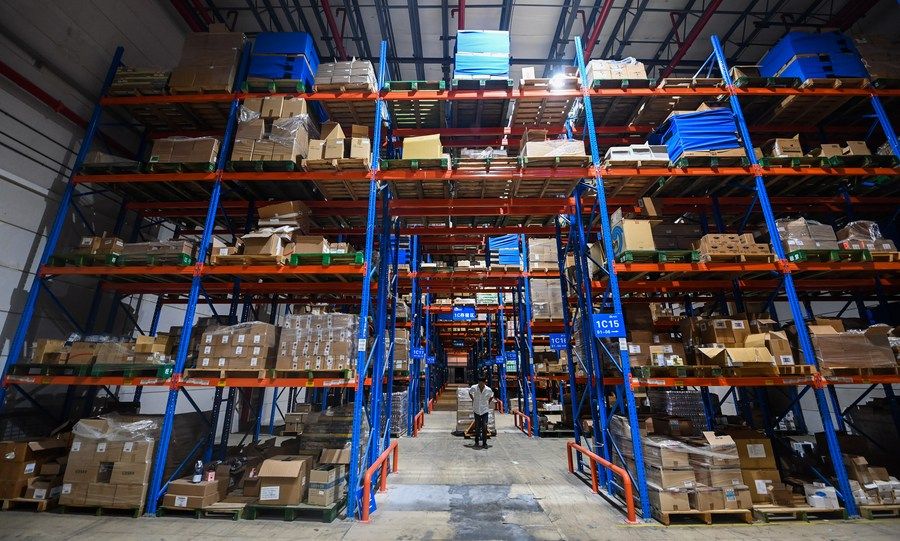

On September 2, 2022, in a cross-border bonded warehouse in Hangzhou Comprehensive Bonded Zone, staff were carrying cross-border e-commerce bonded imported goods. Xinhua News Agency reporter Xu Yushe
According to the data of the General Administration of Customs, the import and export of China by bonded logistics increased by 15.4% in the first four months of this year. Among them, exports increased by 23.4% and imports increased by 10.8%.
According to the Opinions on Accelerating the Development of New Foreign Trade Formats and Models, China strives to achieve the development level of new foreign trade formats and models in the forefront of innovative countries by 2035. Bai Ming believes that the new format and new model have a gradual role in promoting the development of foreign trade, and it is expected to become a "booster" for the stable growth of foreign trade in the long run.
In the first four months, China’s total import and export value to ASEAN, Latin America, Africa and countries along the Belt and Road increased by 13.9%, 10.3%, 17.5% and 16% respectively. Gao Yuning, deputy director of the Institute of International Development and Global Governance of the School of Public Administration of Tsinghua University, believes that under the background of policy support and the positive development of economic and trade relations with traditional trading partners, the contribution of new markets along the "Belt and Road" to trade growth continues to increase.
China’s foreign trade promotes stability and quality improvement. In addition to stabilizing "old customers" and "old friends", it also attaches importance to the expansion of new markets. The the State Council executive meeting held in early April requested that enterprises be guided to further explore the markets of developing countries and ASEAN and other regional markets.

On September 11th, 2021, in Nanning International Convention and Exhibition Center, Guangxi, visitors walked out of the 18th China — ASEAN Expo Pavilion. Xinhua News Agency reporter Lu Boan photo
Boosting the confidence and vitality of foreign trade enterprises has always been the policy focus of China to promote the stable scale and excellent structure of foreign trade. Bai Ming pointed out that due to external factors, China’s foreign trade is still under great pressure this year. It is necessary to implement a combination of policies to stabilize foreign trade and help enterprises stabilize orders and expand the market.
Recently, the General Office of the State Council, China issued the Opinions on Promoting the Stable Scale and Excellent Structure of Foreign Trade, proposing to strengthen trade to promote market expansion, stabilize and expand the import and export scale of key products, increase financial support, accelerate the innovative development of foreign trade and optimize the foreign trade development environment.
"A series of combination punches for stabilizing foreign trade policies are more systematic, comprehensive and comprehensive, which will play a better supporting role in China’s foreign trade development and will promote the stability and quality of foreign trade throughout the year." Gao Yuning said.